What is Research Data Management?
Research Data Management (RDM) refers to various practices aimed at ensuring the quality, accessibility, and (re-)usability of your research data throughout the entire research process. It involves organizing, documenting, storing, and sharing data effectively to support transparent and valid scientific practices.
Why is RDM important?
Effective RDM has numerous benefits. Here are the key advantages and reasons for implementing good data management practices:
- Saves Time and Resources: Well-organized data management increases efficiency by preventing duplicative work, data loss, and reducing research and data storage costs through optimizing data usage. Professionally standardized RDM processes reduce future effort when using the data.
- Ensures Continuity of Research: RDM enables the continuity of research projects, reducing interruptions due to data-related issues for example the loss of knowledge when group members leave the group.
- Makes Your Data Reusable: Well-managed data allow you and others to replicate findings and reuse data for future projects, potentially leading to valuable discoveries.
- Opens Funding Opportunities: Funding sources may require a data management plan as a condition for project eligibility, so good RDM can open up funding opportunities.
FAIR Principles
Since the FAIR Principles were formulated in 2016, they have formed the basis of many funding agencies' data management policies. The term "FAIR" stands for Findability, Accessibility, Interoperability, and Reusability of digital assets. Is your data FAIR? Go and find out:
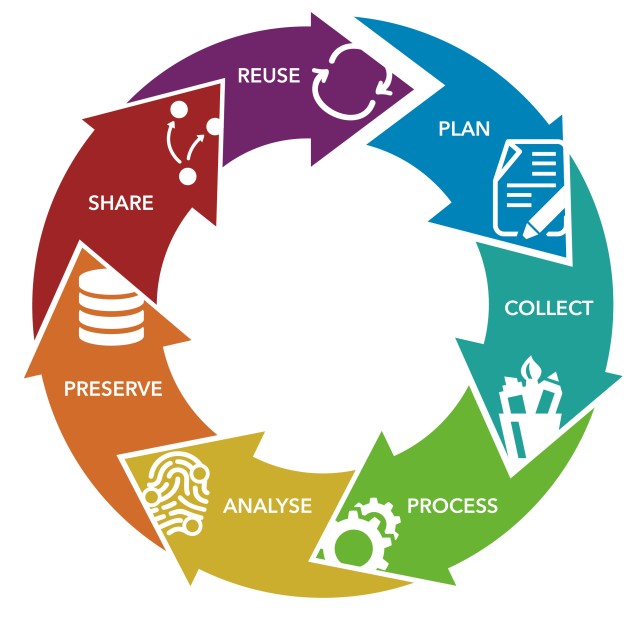
Research Data Lifecycle
The research data lifecycle is like a roadmap for how data in your research project is handled. It shows the different steps data goes through before, during, and after the project. At each step, there are different things to do to manage the data properly, and what you do in one step affects what happens in the next one.
Resources to make you an RDM expert
Planning phase
Possible key questions in this phase: What is my research question? What data do I need to collect to answer this question? How do I plan to handle the collected data throughout its lifecycle? What are the requirements of the funding agencies?
Guide to writing a Data Management Plan
Detailed guide based on the DFG checklist of the NFDI consortium FAIRmat
RDMO: Data Management Plan Use Tool
Free software for structuring and planning the research process developed in a DFG project
DFG Guidelines on the Handling of Research dRata
Detailed Guidelines by the German Research Foundation (DFG)
Guidelines and DMP Template for EU Horizon
Online Manual by the European Commission
Collecting phase
Possible key questions in this phase: How will I document the instruments or methods used for data collection? Which information is required for data interpretation and utilization of the data? What will be raw- and meta- data in my projects and how can I organize their regular collection?
ELN Finder
Helps you to search and select a suitable Electronic Lab Notebook (ELN)
Guide to writing “readme” style metadata
Metadata Standards Catalog
Collaborative, open directory of metadata standards
Processing phase
Possible key questions in this phase: How do I clean the data (e.g. by eliminating noise)? How do I merge data from different sources? What procedures do I use to ensure data quality? How do I document the data processing so that the result can be reproduced from the raw data?
OpenRefine
Open source tool for cleaning and transforming messy data
Analysing Phase
Preserving Phase
Possible key questions in this phase: How do I ensure long-term archiving of my data? Which data should be selected for long-term preservation? Which data format should be selected for long-term preservation?
re3data
Registries/Lists of Data Repositories
Zenodo
Research data repository operated and hosted by CERN and OpenAIRE
Sharing Phase
Possible key questions in this phase: Which repository suits my research best, and what data sharing policies should I take into account? Which user group should have which access rights?
DOI: Digital Object Identifier
Most prominent persistent identifier in science
Orcid: Open Researcher and Contributor Identifier
Persistent identifier for you as a researcher
Creative Commons
Licenses for data sharing
Choose a license
Overview to select a suiting license
re3data
Registries/Lists of Data Repositories
Zenodo
Research data repository operated and hosted by CERN and OpenAIRE
Reusing Phase
Possible key questions for this phase: Can I access my data, and is it possible for me or other researchers to reuse it?
DataCite
Search engine for published data sets
B2find EUDAT
Search engine for published data sets
Meet us at the MCQST Datarama
MCQST Datarama is a best practise talk series to exchange knowledge within the Cluster. This initiative is driven by members for members, with a specific focus on sharing technical solutions and expertise. Stay tuned for future dates.
RDM Workshops
Research Data Management Basics
Training session offering an introduction to research data management (RDM) by the TUM Research Data Hub.
Research Data Management Basics
Training session offering an introduction to research data management (RDM) by the TUM Research Data Hub.
MCQST Research Data Management Workshop
Join us for an introductory Research Data Management (RDM) Workshop tailored for MCQST members.
